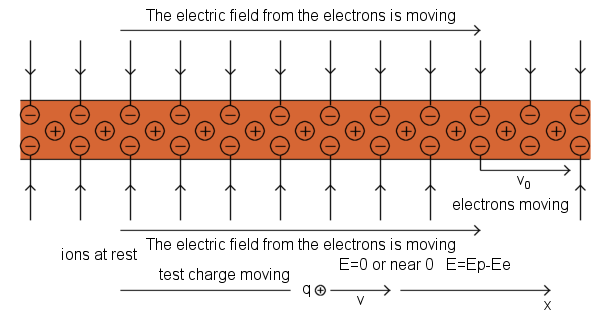
Calculations for my nuclear fusion reactor ring - the charge accumulated in half the ring and the average angle of interaction is 45° - the average value of the sine function from 0 to 180 degrees is 2 ÷ pi, so we multiply the charge interaction of half the ring by 2 ÷ pi and compare the Coulomb electric force from half the ring to the Lorentz magnetic force of the strongest magnets.
ITER magnet to be 13 T
Wendelstein 7-X magnets 6-15 T
MIT magnet 20 T
Chinese magnets 21.7 - 35.1 T
Tokamak Energy magnets 24.4 T
The velocity of a deuteron with kinetic energy of 1 MeV is approximately 9.79 × 10⁶ m/s
Maximum Lorentz magnetic force F = q × V × B
Deuteron charge 1.602176634×10^−19 C
The velocity of a deuteron with kinetic energy of 1 MeV is approximately 9.79 × 10⁶ m/s
Magnetic flux density also called magnetic B-field strength from 6 to 35.1 T
Checking the Lorentz magnetic force for 22 and 35 T
F 22 T = 1.602176634×10^−19 × 9.79 × 10^6 × 22 = 3.45076803 × 10^-11 newton N
F 35 T = 1.602176634×10^−19 × 9.79 × 10^6 × 35 = 5.48985824 × 10^-11 newton N
F 35.1 T = 1.602176634×10^−19 × 9.79 × 10^6 × 35.1 = 5.50554355 × 10^-11
Coulomb electric force F = q × E
Electric field intensity due to half the charged ionized ring E = 2 ÷ π × k × Q ÷ r^2 = 2 ÷ π × 1 ÷ ( 4 π × ε₀ ) × Q ÷ r^2
Q electric charge of half the charged ionized ring
Electric field intensity required to produce the equivalent magnetic force on a deuteron with a velocity of approximately 9.79 × 10⁶ m/s in a magnetic field of 35.1 tesla T
E = F ÷ q
F = 5.50554355 × 10^-11 newton N
q Charge of deuteron 1.602176634×10^−19 C
E = 5.50554355 × 10^-11 ÷ ( 1.602176634×10^−19 ) = 343,629,000.27164 N / C newton / coulomb
E = 2 ÷ π × 1 ÷ ( 4 π × ε₀ ) × Q ÷ r^2
Q = E × π ÷ 2 × 4 π × ε₀ × r^2 = E × π^2 × 2 × ε₀ × r^2
E = 343,629,000.27164 N / C
ε₀ = 8.854187812813 × 10^−12 F/m
Q = 343,629,000.27164 × π^2 × 2 × 8.854187812813 × 10^−12 × 0.16^2 = 343,629,000.27164 × π^2 × 2 × 8.8541878128 × 10^−12 × 0.16^2 = 0.0015374756 C
It's a bit low, I'll check later, but if there's no mistake, it's shockingly low
* edit 2 Additional data check
According to the data validation / correctness analysis using ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot, the maximum confirmed real surface charge density σ = ~ 10^-3 C / m², i.e. 0.001 C/m², so if the limit is the surface charge density σ = ~ 0.001 C/m², it is enough to increase the surface of the metal elements or the metal part of the ring and it is possible to obtain the calculated charge of half of the ring Q = 0.0015374756 C - if it is not possible to charge the ring more by charging its elements on both sides, then with dimensions of 1 m circumference - radius about 16 cm, diameter about 32 cm and ring width about 10 - 20 cm or even 30 cm, you can do * edit 2 × 6 - 7 - 10 - 20 = 12 - 13 - 14 - 20 - 40 layer ring, and if when loading on both sides the surface area of both sides counts, you can make fewer layers or reduce the dimensions and you can easily get the surface * edit 2 × 2 m² = 4 m².


For comparison, I previously calculated that a mini piece of copper measuring 1 mm by 1 mm by 1 mm can be charged
Q = 13.5664942388 coulombs C
At an ionization voltage of
U = 33,928,277.445413 V
13.5664942388 C ÷ 0.0015374756 C = 13.5664942388 ÷ 0.0015374756 = 8,823.8761244731 times less charge, so we calculate how much we can reduce the ionization voltage and the dimensions of the copper piece to maintain a charge of 0.0015374756 C
cube root cbrt(8,823.8761244731) = 20.6642573027 times
U = 33,928,277.445413 V ÷ 20.6642573027 = 33,928,277.445413 ÷ 20.6642573027 = 1,641,882.2582595 volts V
So instead of using expensive, energy-intensive electromagnets with a magnetic flux density also called magnetic B-field strength of, for example, 35.1 Tesla T, simply use a charged ionized ring - a voltage of 1,641,882.2582595 volts V is enough.
For comparison, small pocket-sized stun guns available on the market can have a voltage of 50-98 million volts V, and a lightning bolt can have a voltage of 100 million to 1 billion volts V.
5 Liters of Copper × 8.935 kg/L = 44.675 kg
44.675 kg × 80 PLN/kg = 3,574 PLN + cost of ionizer, inverter and other accessories
Semi half mechanical electromechanical magnet electromagnet
The speed of electrified elements incorporated into a rotating disk or ring or roller or cylinder or cone or dome or sphere or ball or segments of a rotating disk, or simply the electrified disk itself, e.g. with a gap blocking the circular flow of charge, can be e.g. 16.67 metre per second ( m/s ) and this is already at a rotational speed of 1000 revolutions per minute ( rpm, rev/min, r/min, r·min−1 ). For comparison, the electron drift speed ( electron drift velocity ) in a conductor or the speed of super- current in a superconductor is in the range of 0.1 to 1 millimeter per second. In addition, instead of increasing the percentage charge of the disk elements or the disk itself, the amount of moving charge can be increased by increasing the volume of the charged disk elements or the disk itself.

Semi half mechanical electromechanical magnet electromagnet
The strongest electromagnet in the world semi half mechanical electromechanical magnet electromagnet electro mechanical the most powerful
Concept of electromechanical electromagnet with lower energy consumption and greater strength than commonly known magnets, which could enable the construction of cheaper hydrogen fusion reactors, the construction of spaceships with greater range, enable the levitation of larger animals than in Bitter's magnets and facilitate the construction of boats, ships, and boards levitating above the water with lower power consumption. An electromechanical electromagnet ( semi-mechanical electromagnet ) is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by a rotating ring or e.g. disk e.g. with charged elements incorporated and e.g. at a rotational speed of 1000 rpm provide a speed of electrons or positive ions e.g. 16.67 m/s with a diameter of about 32 cm / 12.6 inches.
For comparison, the electron drift speed ( electron drift velocity ) in a conductor or the speed of super- current in a superconductor is in the range of 0.1 to 1 millimeter per second.
In addition, instead of increasing the percentage charge of the ring or disk elements, the amount of moving charge can be increased by increasing the volume of the charged ring or disk elements
* edit I'm adding calculations
The formula for the drift velocity of electrons in a conductor is u=I/nAe, therefore the equivalent current is I=unAe
u - drift velocity of electrons or positive ions in a rotating charged ring or disk = 2πr × rpm. / min / 60
n - number of electrons per cubic meter = Avogadro's constant × number of moles per cubic meter × number of ionized valence electrons
e.g., for copper, e.g., with 1 electron ionized per atom, the number of ionized electrons n per cubic meter = 6.02214076×10^23 mol^-1 × 140,606.80451956 mol/m^3 × 1 = 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3
A - cross-section
e.g., for a ring or disk with a diameter of about 32 cm, i.e., a radius of 0.16 m, the circumference is about 1 meter, and e.g., 5 liters of copper = 0.005 m^3 of copper = 0.005 m^3 / about 1 meter = about 0.005 m^2
The thickness of such a ring is √(0.005 m^2) = 0.0707 m, or 7.07 cm
e - elementary charge of the electron = -1.602176634×10^−19 C
I - equivalent current = unAe = 16.67 m/s × 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 × 0.005 m^2 × 1.602176634×10^−19 C = 16.67 × 8.46753969×10^28 × 0.005 × 1.602176634×10^−19 = 1,130,767,294.8028 amps
For comparison, the current in a Bitter electromagnet with a magnetic induction of 16 Tesla during operation is about 20,000 amps.
1,000,000,000 amps / 20,000 amps = 50,000 times greater equivalent current than the current in a Bitter 16 Tesla magnet. However, Bitter magnets can contain about 1,000 current-carrying plates, so with 1 rotating charged ring or disk with the previously given dimensions of 7.07 × 7.07 cm and a circumference of 1 m, the current difference is about 50 times. In addition, on the one hand, a 7 cm ring is about 4-8 times thinner than a stack of 1,000 plates, which increases the density of the magnetic field. On the other hand, the hole in the center of the ring or disk has, for example, about 60 times greater surface area than in a Bitter electromagnet, which in turn reduces the density of the magnetic field
50 × 16 tesla = 800 tesla T
800 tesla ÷ 7.5 or 15 = 106.67 or 53.33 tesla T
However, due to the opposing motion of charges on the left and right sides of the ring or disk, magnetic forces tear the ring or disk apart. Furthermore, magnetic forces compress the ring or disk in a direction parallel to its axis, and one must limit oneself, for example, to 80 tesla T to avoid damaging the disk.
In tests to destroy the ring or disk, it can be spun up to speeds of over 100,000 - 300,000 rpm and theoretically achieve a magnetic induction of over 80,000 - 240,000 tesla T ÷ 7.5 or 15 = 5,333.33 - 32,000 tesla T
Calculating the voltage needed to ionize a metal ring or disk, e.g., made of copper.
Based on the density of copper according to the popular version of 8935 kg/m^3, the molar atomic mass of copper of 63.546 g/mol, and the Avogadro constant of 6.02214076×10^23 mol^−1, I first calculate the number of copper atoms per cubic meter and the thickness of 1 atom in a copper block: 8935000 g/m3 ÷ 63.546 g/mol = 140,606.80451956 mol/m^3.
140,606.80451956 mol/m^3 × 6.02214076×10^23 mol^−1 = 8.46753969 × 10^28 atoms / m^3
Cubic root cbrt(8.46753969×10^28) = 4,391,225,573.3491 atoms / m
Thickness of 1 atom in a copper block = 1 m ÷ 4,391,225,573.3491 atoms/m = 0.227726857 × 10^-9 m or nanometer
With one ionizer connection on the opposite side of the gap in the ring
the ionizing voltage has to travel through a 0.5 m thick row of atoms.
0.5 m × 4,391,225,573.3491 atoms/m = 2,195,612,786.6746 atoms from the ionizer connection point to the gap in the disc.
Based on the ionization energy, I assume the ionization voltage of 1 copper atom is 7.72638 V. You can also check the voltages of 4.53 - 5.10 V based on the work function.
7.72638 V × 2,195,612,786.6746 atoms = 16,964,138,722.707 V.
So the disk must be divided along the circumference into at least 100 or better 200 parts, the thickness and width into 14.14 or 28.28 parts, i.e. into at least 100 - 200 × 14.14 × 14.14 = 19,993.96 - 39,987.92 parts or better 200 - 400 × 28.28 × 28.28 = 159,951.68 - 319,903.36 parts to reduce the ionization voltage from 16.96 billion volts V to at least 169.64 million volts V or e.g. 84.82 million volts V.
For comparison, small pocket stun guns available on the market can have a voltage of 50 - 98 million volts V, and lightning can have a voltage of from 100 million to 1 billion volts
5 liters of copper × 8.935 kg/L = 44.675 kg
44.675 kg × 80 PLN/kg = 3,574 PLN + the cost of the ionizer, inverter, and other accessories
Calculations
Q - electric charge = number of added or subtracted electrons / m^3 × volume x elementary charge of electron =
8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 × 0.000000001 m^3 × 1.602176634×10^−19 C = 8.46753969×10^28 × 0.000000001 × 1.602176634×10^−19 = 13.5664942388 coulombs C
Side length of a piece of copper block = Cube root of 0.000000001 m^3 = cbrt(0.000000001) = 0.001 m or 1 millimeter mm
0.001 m × 4,391,225,573.3491 atoms/m = 4,391,225.5733491 atoms
Based on the ionization energy, I assume the ionization voltage of 1 copper atom is 7.72638 V. You can also check the voltages of 4.53 - 5.10 V based on the work function.
4,391,225.5733491 atoms × 7.72638 V = 33,928,277.445413 V
13.5664942388 C × 33,928,277.445413 V = 13.5664942388 × 33,928,277.445413 = 460,287,780.4956 joules J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
460,287,780.4956 J ÷ 360,000,000 J = 460,287,780.4956 ÷ 360,000,000 = 1.278577168 times greater/higher capacity, so we calculate how much we can reduce the ionization voltage and the dimensions of the copper piece to maintain 100 kWh of capacity. √(√(1.278577168)) = 1.0633634685 times
33,928,277.445413 V ÷ 1.0633634685 = 31,906,566.710697 volts V, therefore, the copper piece is smaller than 0.000001 liters, i.e. 0.000001 × 8.935 kg/L = 0.000008935 kg = 0.008935 g or many smaller pieces of copper may one day replace other batteries at voltages as low as 31,906,566.710697 volts V
5 Liter Copper Block as a Battery
Calculations
Q - electric charge = number of electrons added or subtracted / m^3 × volume x elementary charge of the electron =
8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 × 0.005 m^3 × 1.602176634×10^−19 C = 8.46753969×10^28 × 0.005 × 1.602176634×10^−19 = 67,832,471.193928 C
Side length of the copper block = Cube root of 0.005 m^3 = cbrt(0.005) = 0.1709975947 m
0.1709975947 m × 4,391,225,573.3491 atoms/m = 750,889,010.82782 atoms
750,889,010.82782 atoms × 7.72638 V = 5,801,653,835.4799 V
67,832,471.193928 C × 5,801,653,835.4799 V = 67,832,471.193928 × 5,801,653,835.4799 = 3.93540517 × 10^17 J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
3.93540517 × 10^17 J ÷ 360,000,000 J = 3.93540517 × 10^17 ÷ 360,000,000 = 1,093,168,102.7778 times greater/higher capacity, so we calculate how much we can reduce the ionization voltage and the dimensions of the copper piece to maintain 100 kWh of capacity: √(√(1,093,168,102.7778)) = 181.8325954245 times
5,801,653,835.4799 V ÷ 181.8325954245 = 31,906,566.707336 volts V, so the copper block 6,011,947.9690954 times smaller than 5 liters, i.e. 5 ÷ 6,011,947.9690954 × 8.935 kg/L = 0.000007431 kg = 0.007431 g or many smaller pieces of copper may one day replace other batteries with voltages of 31,906,566.710697 volts V
Calculations for a battery voltage of 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, 5000, ... volts V
1000 V / 7.72638 V = 129.4267172984 atoms
129.4267172984 atoms × thickness of 1 atom in a copper block 0.227726857 × 10^-9 m = 29.4739395×10^-9 m or about 30 nanometers
(29.4739395×10^-9)^3 × 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 = 2,168,062.5322705 atoms and electrons in a cube with sides 30 nanometers
Charge = 2,168,062.5322705 × 1.602176634×10^-19 = 3.47361913×10^-13 coulombs C
Capacity = Charge × Voltage
3.47361913×10^-13 × 1000 = 3.47361913×10^-10 joules J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
360,000,000 ÷ (3.47361913×10^-10) = 1.03638305×10^18 or a quintillion nano pieces of copper
2000 V ÷ 7.72638 V = 258.8534345968 atoms
258.8534345968 atoms × thickness of 1 atom in a copper block 0.227726857 × 10^-9 m = 58.9478791×10^-9 m or about 59 nano meters
(58.9478791×10^-9)^3 × 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 = 17,344,500.346435 atoms and electrons in a cube with sides 58.9 nano meters
Charge = 17,344,500.346435 × 1.602176634×10^-19 = 2.77889532×10^-12 coulombs C
Capacity = Charge × Voltage
2.77889532×10^-12 × 2000 = 5.55779064×10^-9 joules J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
360,000,000 ÷ (5.55779064×10^-9) = 6.47739405×10^16 or about 65 quadrillion nano pieces of copper
1 cent for less than 1 grams of copper + cost of ionizer, inverter and other accessories
This is calculated for a discharge to the ground - if it is not possible to discharge to the ground, you need to divide this piece of the block into 2 parts or add a second piece of the block.
3000 V ÷ 7.72638 V = 388.2801518952 atoms
388.2801518952 atoms × thickness of 1 atom in a copper block 0.227726857 × 10^-9 m = 88.4218186×10^-9 m or about 88.4 nanometers
(88.4218186×10^-9)^3 × 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 = 58,537,688.569913 atoms and electrons in a cube with sides 88.4 nanometers
Charge = 58,537,688.569913 × 1.602176634×10^-19 = 9.37877168×10^-12 coulombs C
Capacitance = Charge × Voltage
9.37877168×10^-12 × 3000 = 2.81363150×10^-8 joules J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
360,000,000 ÷ (2.81363150×10^-8) = 1.27948525×10^16 or about 12.8 quadrillion nano pieces of copper
4000 V ÷ 7.72638 V = 517.7068691936 atoms
517.7068691936 atoms × thickness of 1 atom in a copper block 0.227726857 × 10^-9 m = 117.895758×10^-9 m or about 117.9 nano meters
(117.895758×10^-9)^3 × 8.46753969×10^28 m^-3 = 138,756,002.06531 atoms and electrons in a cube with sides 117.9 nano meters
Charge = 138,756,002.06531 × 1.602176634×10^-19 = 22.2311624×10^-12 coulombs C
Capacity = Charge × Voltage
22.2311624×10^-12 × 4000 = 8.89246496×10^-8 joules J
A 100 kWh battery has 360,000,000 joules J
360,000,000 ÷ (8.89246496×10^-8) = 4.04837131×10^15 or about 4 quadrillion nano Copper pieces
5 Liters of copper × 8.935 kg/L = 44.675 kg
44.675 kg × 80 PLN/kg = 3,574 PLN + the cost of the ionizer, inverter, and other accessories
Radiation by an accelerated charge
Alternating magnetic field, electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic induction
An electric field moves with the velocity that the particle had while emitting that field.


Electric field of a charge that stops
Suppose a charge q has been moving at constant speed v0 in the x direction for a long time. Suddenly it stops after a short period of constant deceleration. Electric field of a charge travels radially outward and moves with the velocity that the charge had while emitting that field.
The velocity versus time graph

The electric field
Assuming that the v0 ≪ c, we can neglect the relativistic compression of the field lines. Time t=0 it was the moment when deceleration began, and position x=0 it was the position of the particle at that moment. The particle has been moved a little farther on before coming to a stop, Δx=1/2*v0Δt1. That distance is very small compared with the other distances in the picture.
We now examine the electric field at a time t=Δt2≫Δt1. The electric field reaches a distance R=cΔt2. Thus, the field at a distance greater than R=cΔt2, in region I must be a field of a charge which has been moving and is still moving at the constant speed v0. That field appears to come from the point x=v0Δt2 on the x axis. That is where the particle would be now if it hadn't stopped. On the other hand, the field at a distance less than c(Δt2-Δt1), in region II must be a field of a charge at rest close to the position x=0 (exactly at x=1/2*v0Δt1).

What must the field be like in the transition region, the spherical shell of thickness cΔt1 between region I and region II? A field line segment AB lies on a cone around the x axis which includes a certain amount of flux from the charge q. Due to the Gauss' law, if CD makes the same angle θ with the axis, the cone on which it lies includes that same amount of flux. (Because the v0 ≪ c, we can neglect the relativistic compression of the field lines.) That's why AB and CD must be parts of the same field line, connected by a segment BC. The line segment BC shows us the direction of the filed E within the shell. This field E within the shell has both a radial component Er and a transverse component Eθ. From the geometry of the figure their ratio is easily found.

(1)
Due to the Gauss' law, E
r must have the same value within the shell thickness that it does in region II near B. That's why E
r=q/4πε
0R
2=q/4πε
0c
2Δt
22, and substituting this in Eq. 1 we obtain

(2)
And v
0/Δt
1 = a, the magnitude of the (negative) acceleration, and cΔt
2= R, so our result can be written

(3)
A remarkable fact is here revealed: Eθ is proportional to 1/R, not to 1/R2! As time goes on and R increases, the transverse field Eθ will eventually become very much stronger than Er. Accompanying this transverse (that is, perpendicular to R) electric field will be a magnetic field of equal strength perpendicular to both R and E. This is a general property of an electromagnetic wave.
We now calculate the energy stored in the transverse electric field above, in the whole spherical shell. The energy density is

(4)
The volume of the shell is 4πR
2cΔt
1, and the average value of sin
2θ over a sphere is 2/3. The total energy of the transverse electric field is consequently

(5)
To this we must add an equal amount for the energy stored in the transverse magnetic field:
Total energy in transverse electromagnetic field is

(6)
The radius R has canceled out. This amount of energy simply travels outward, undiminished, with speed c from the site of the deceleration. Since Δt
1 is the duration of the deceleration, and is also the duration of the electromagnetic pulse a distant observer measures, we can say that the power radiated during the acceleration process was

(7)
As it is the square of the instantaneous acceleration that appears in Eq. 7, it doesn't matter whether a is positive or negative. Of course it ought not to, for stopping in one inertial frame could be starting in another. Speaking of different frames, P
rad itself turns out to be Lorentz-invariant, which is sometimes very handy. That is because P
rad is energy/time, and energy transforms like time, each being the fourth component of a four-vector. We have here a more general result than we might have expected. Equation 7 correctly gives the instantaneous rate of radiation of energy by a charged particle moving with variable acceleration-for instance, a particle vibrating in simple harmonic motion. It applies to a wide variety of radiating systems from radio antennas to atoms and nuclei.
Radiating Charge simulation - PhET INTERACTIVE SIMULATIONS
Purcell appendix B in the CGS system















 (1)
(1) (2)
(2) (3)
(3) (4)
(4) (5)
(5) (6)
(6) (7)
(7)














